GPU Computing
Recently, the common desktop CPUs (central processing units) consist of a few cores (typically 4 cores) optimized for sequential execution while GPUs (graphics processing units) present massively parallel architectures including thousands of smaller processing units (called cores) and very high-memory bandwidths. These GPU architectures are becoming increasingly efficient for dealing with compute-intensive workloads, offering high speedups when compared to CPUs. To overcome the main obstacle regarding the developments of parallel programs on GPUs, the CUDA programming interface and framework emerged the dissemination of a worldwide new parallel programming style, based on extensions to the C language, and accessible by a broader community of programmers and corresponding new application models.
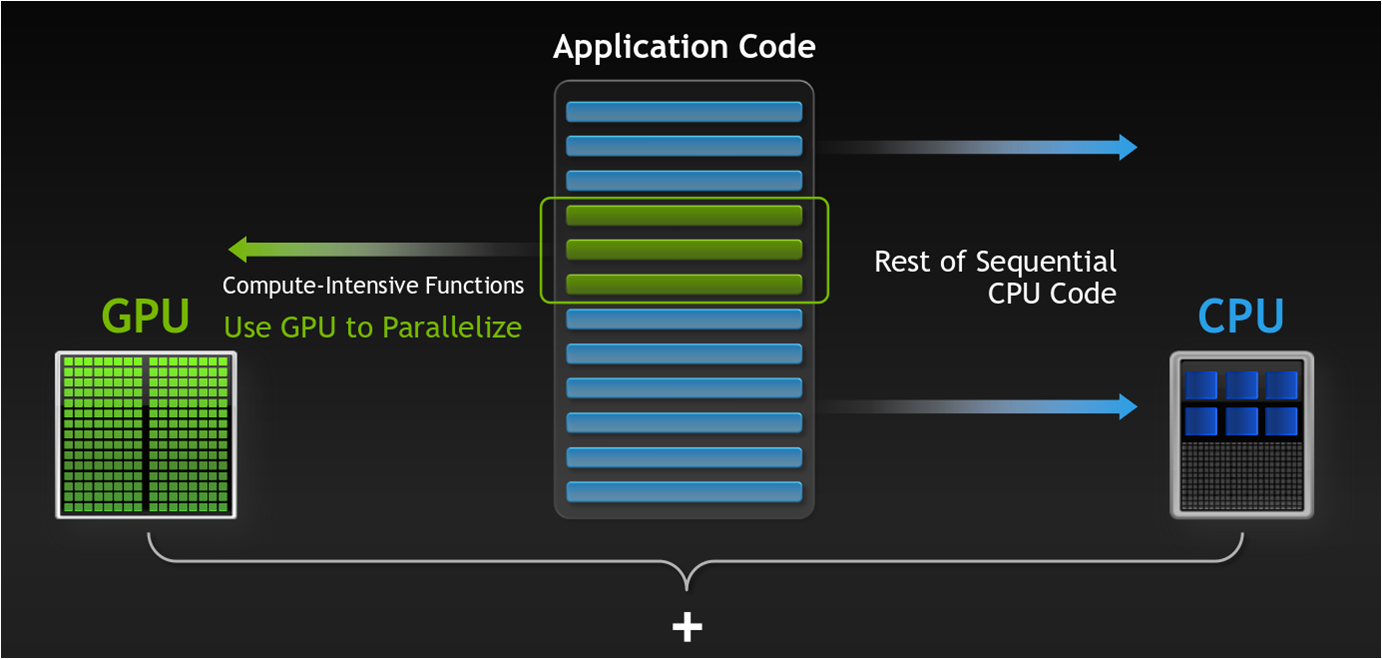
(Workload distribuition between CPU and GPU)
GPU VS CPU
In this section, we will show the most important technical characteristics. With this, we can see some of the reasons that support the use of parallel processing on the GPU. A simple comparison is made below:
|
 |
|
 |
CPU Analogy:
GPU Analogy:






